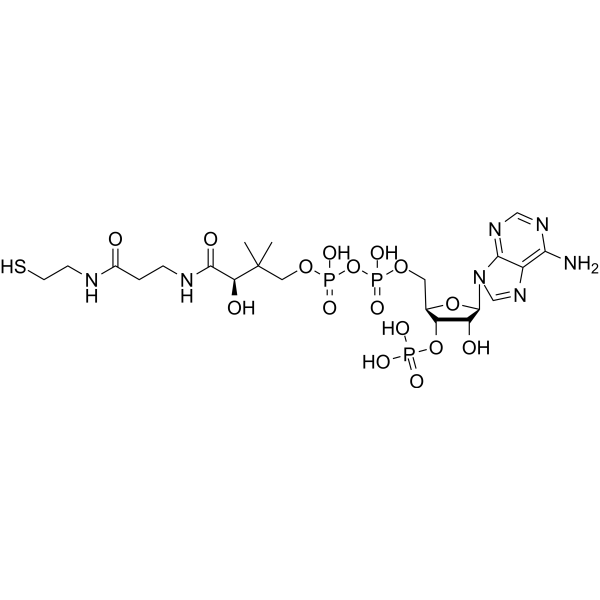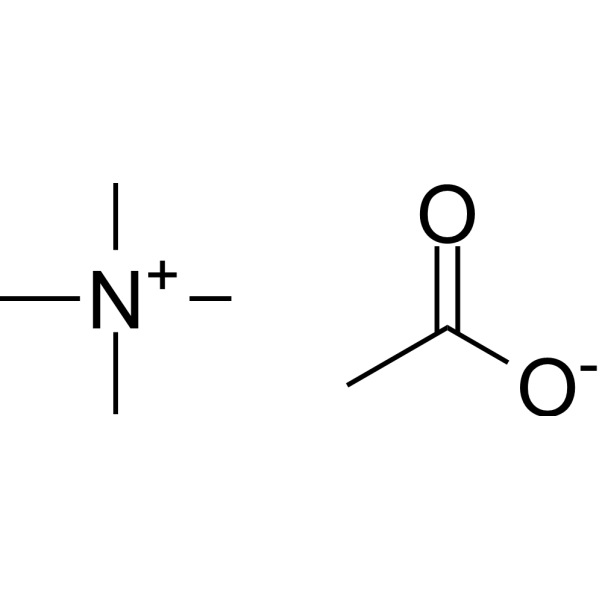Search Result
Results for "
carboxylic acids
" in MedChemExpress (MCE) Product Catalog:
7
Biochemical Assay Reagents
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Areas |
Chemical Structure |
-
- HY-W269179
-
|
|
Fluorescent Dye
|
Cancer
|
|
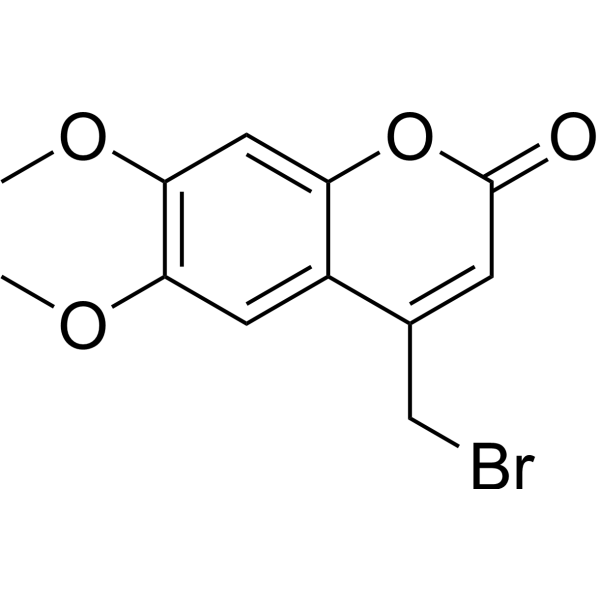
4-Bromomethyl-6,7-dimethoxycoumarin is a fluorescent label for carboxylic acids in chromatographic detection .
|
-
-
- HY-P2947
-
|
Aldehyde dehydrogenase (NAD(P))
|
Aldehyde Dehydrogenase (ALDH)
|
Others
|
|
ALDH (Aldehyde dehydrogenase (NAD(P))) catalyzes the oxidation of aldehydes into their corresponding carboxylic acids with the concomitant reduction of the cofactor NAD(P) into NAD(P)H, is often used in biochemical studies. The ALDHs are one of many enzyme systems the body utilizes to alleviate aldehyde stress .
|
-

-
- HY-W098280
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
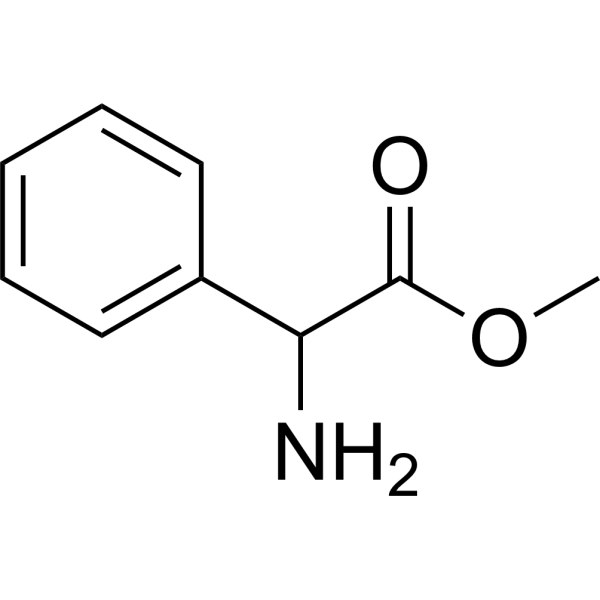
Phenylglycine methyl ester is a chiral anisotropic reagent. Phenylglycine methyl ester can be used for absolute configuration determination of various chiral carboxylic acids .
|
-
-
- HY-D0035
-
|
|
Fluorescent Dye
|
Others
|
|
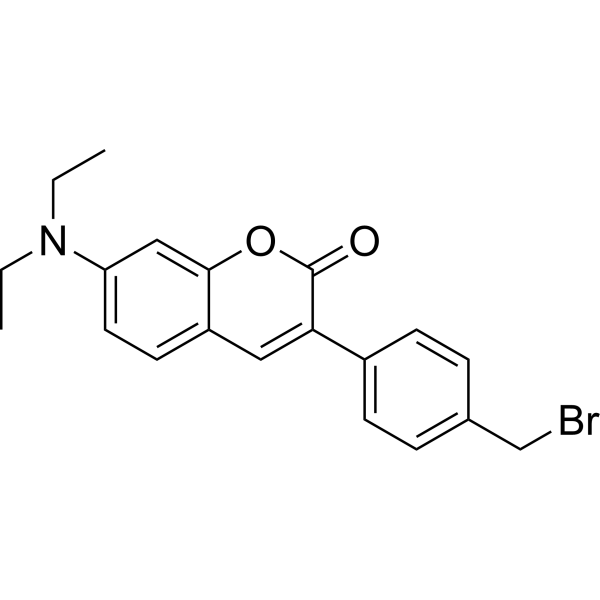
MPAC-Br is a highly sensitive fluorescent derivatization reagent for carboxylic acids in HPLC .
|
-
-
- HY-D0115
-
|
|
DNA Stain
|
Others
|
|
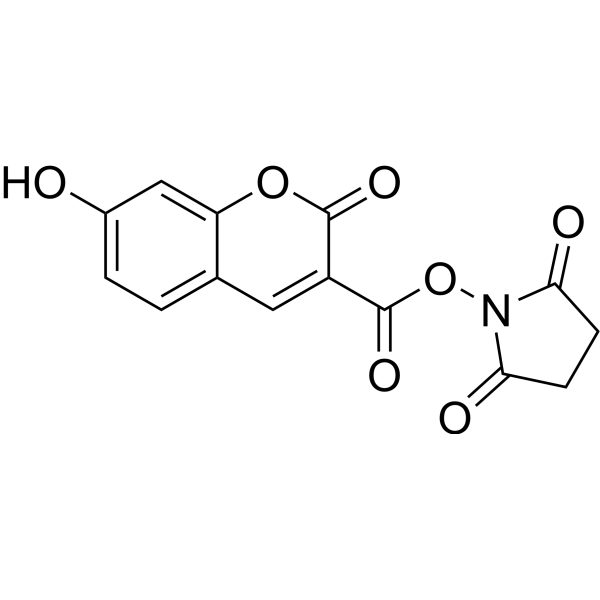
7-Hydroxycoumarin-3-carboxylic acid N-succinimidyl ester is the amine-reactive succinimidyl ester of 7-Hydroxycoumarin-3-carboxylic acid. 7-Hydroxycoumarin-3-carboxylic acid N-succinimidyl ester is a blue fluorescent dye for labeling proteins and nucleic acids .
|
-
-
- HY-D1970
-
|
|
Fluorescent Dye
|
Others
|
|
ATTO 700 Cadaverin is a cadaverine derivative of ATTO 700 for reactions of carboxylic acids, aldehydes and ketones with maximum excitation/emission wavelengths: 700/716 nm.
|
-

-
- HY-147180
-
|
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
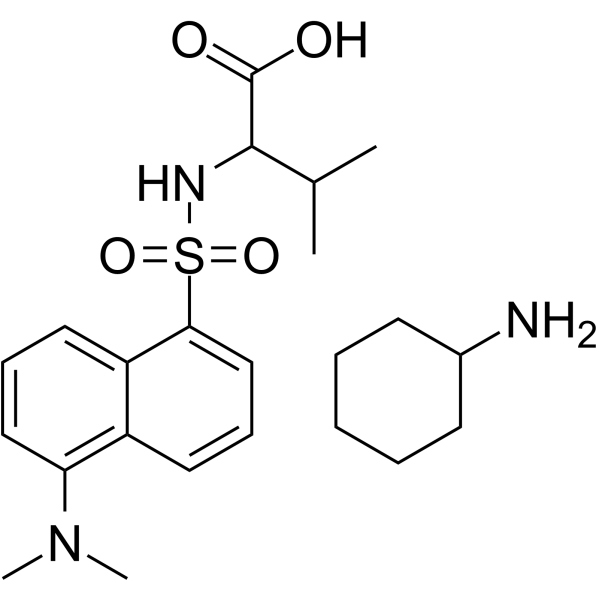
Dansyl-DL-valine cyclohexylammonium is a salt form of Dansyl-DL-valine. Dansyl-DL-valine cyclohexylammonium can be used as analyte in chromatographic separation and separation column for the separation of enantiomers and diastereomers for dansyl amino acids, aromatic carboxylic acids, and isoxazolines .
|
-
-
- HY-135717
-
|
|
Others
|
Cancer
|
|
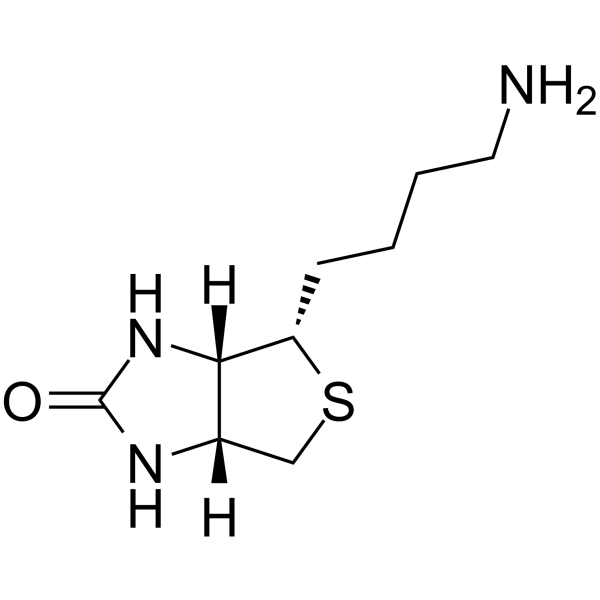
Norbiotinamine is an alternative to biotin. Norbiotinamine can be coupled with a carboxylic group of amino acids to give inverse peptides, having the amide linkage oriented in the opposite direction .
|
-
-
- HY-135717A
-
|
|
Others
|
Cancer
|
|
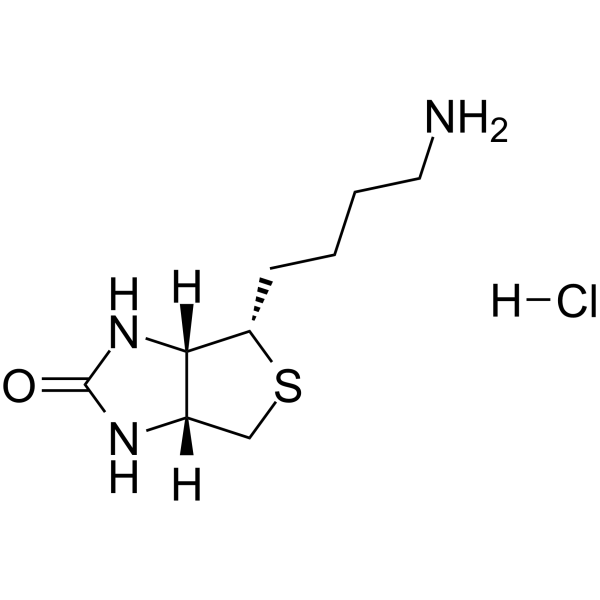
Norbiotinamine hydrochloride is an alternative to biotin. Norbiotinamine can be coupled with a carboxylic group of amino acids to give inverse peptides, having the amide linkage oriented in the opposite direction .
|
-
-
- HY-128851
-
|
|
Fatty Acid Synthase (FASN)
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
Coenzyme A (CoASH) is a ubiquitous and essential cofactor, which is an acyl group carrier and carbonyl-activating group for the citric acid cycle and fatty acid metabolism. Coenzyme A plays a central role in the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle and the metabolism of carboxylic acids, including short- and long-chain fatty acids .
|
-
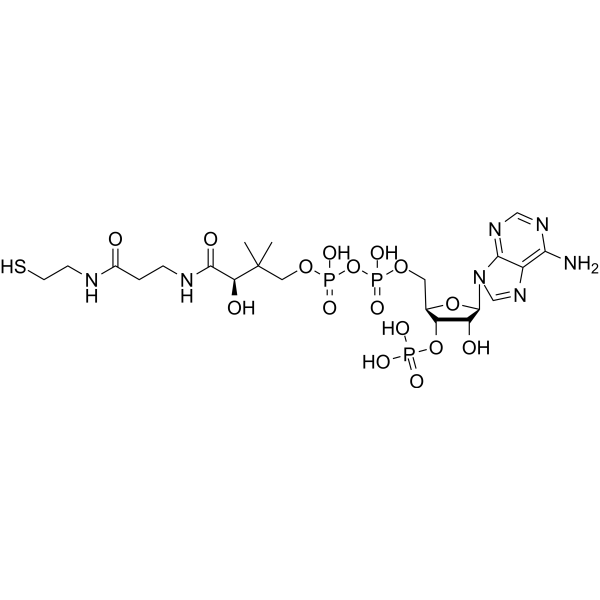
-
- HY-128851A
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
Fatty Acid Synthase (FASN)
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
Coenzyme A (CoASH) is a ubiquitous and essential cofactor, which is an acyl group carrier and carbonyl-activating group for the citric acid cycle and fatty acid metabolism. Coenzyme A plays a central role in the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle and the metabolism of carboxylic acids, including short- and long-chain fatty acids .
|
-
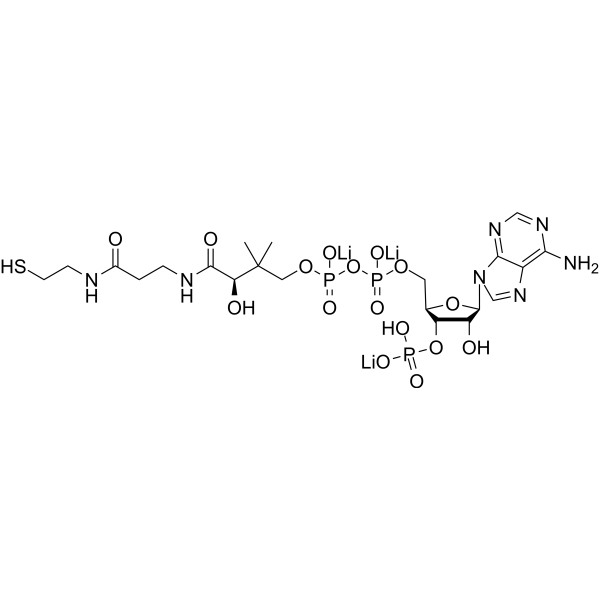
-
- HY-128851B
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
Fatty Acid Synthase (FASN)
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
Coenzyme A (CoASH) sodium is a ubiquitous and essential cofactor, which is an acyl group carrier and carbonyl-activating group for the citric acid cycle and fatty acid metabolism. Coenzyme A plays a central role in the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle and the metabolism of carboxylic acids, including short- and long-chain fatty acids .
|
-
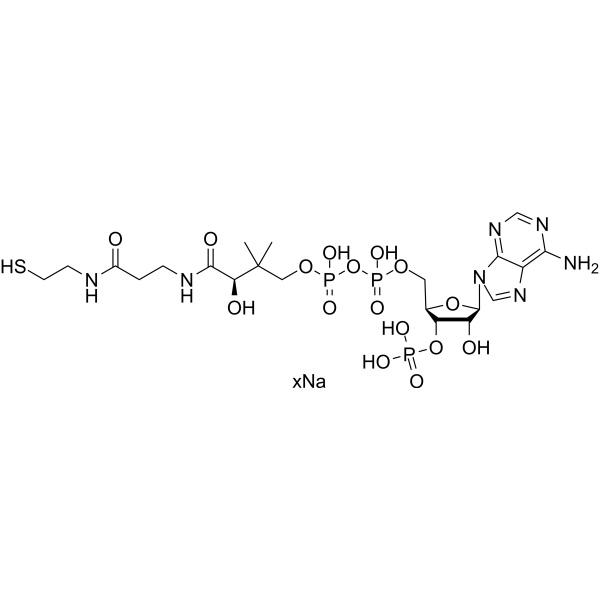
-
- HY-P2831
-
|
CESs
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
Esterase, pig liver (CESs), namely carboxylate hydrolases, are widely distributed in nature, commonly found in mammalian liver, and often used in biochemical research. Esterase catalyzes the hydrolysis of a variety of endogenous and exogenous substrates, including esters, thioesters, carbamates, and amides, hydrolyzing carboxylic acid esters to the corresponding alcohols and carboxylic acids .
|
-
-
- HY-P2736
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
Amidases, a member of nitrilase superfamily, catalyzes the hydrolysis of an amide, leading to the formation of carboxylic acid and ammonia. Amidases contain a conserved stretch of approximately 130 amino acids known as the AS sequence, and play a role in important metabolic processes .
|
-

-
- HY-D1658
-
|
|
Fluorescent Dye
|
Others
|
|
BDP 581/591 amine hydrochloride is a BODIPY dye linker. BDP 581/591 is a universal, photostable fluorophore. The addition of the amine group allows for the compound to react with carboxylic acids, activated NHS esters and other carbonyl groups .
|
-
-
- HY-D0036
-
|
4-Bromomethyl-7-methoxycoumarin
|
Fluorescent Dye
|
Others
|
|
Br-Mmc (4-Bromomethyl-7-methoxycoumarin) is often used as fluorescent label for the determination of compounds possessing a carboxylic group. Br-Mmc is used for the determination fatty acids by TLC or HPLC .
|
-
-
- HY-W013151
-
|
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
1-Pyrenebutyric acid N-hydroxysuccinimide ester (PANHS) is a linker which can be used to fabricate some electrochemical biosensors. 1-Pyrenebutyric acid N-hydroxysuccinimide ester is commonly found in organic chemistry or biochemistry where it is used as an activating reagent for carboxylic acids .
|
-
-
- HY-133022
-
|
(E)-2-Undecenoic acid; (E)-Undec-2-enoic acid
|
Others
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
trans-2-Undecenoic acid ((E)-2-Undecenoic acid) is an α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid and is characterized by acid dimers. The corresponding dimers are connected via intermolecular hydrogen bonds of the carboxylic groups C=O···H-O .
|
-
-
- HY-135500
-
|
|
Endothelin Receptor
|
Endocrinology
|
|
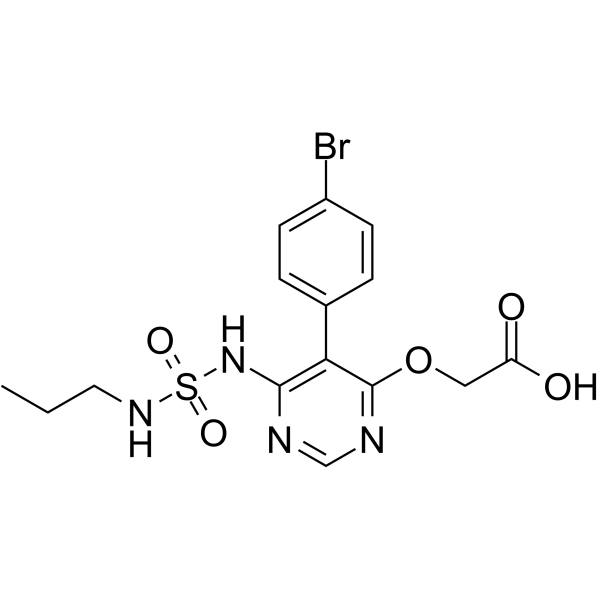
ACT-373898 is an inactive carboxylic acid metabolite of Macitentan. Macitentan is an orally active, non-peptide dual ETA and ETB (endothelin receptor) antagonist .
|
-
-
- HY-D1821
-
|
VF 750 carboxylic acid(free acid)
|
Fluorescent Dye
|
Others
|
|
Vari Fluor 750 Carboxylic acid (VF 750 Carboxylic acid) free acid is a carboxylic acid derivative of Vari Fluor. Vari Fluor carboxylic acid derivatives are unactivated labeled fluorescent dyes for protein, antibody, and polysaccharide labeling that require carboxylic acid activation for use .
|
-

-
- HY-D1822
-
|
VF 555 carboxylic acid(free acid)
|
Fluorescent Dye
|
Others
|
|
Vari Fluor 555 Carboxylic acid (VF 555 Carboxylic acid) free acid is a carboxylic acid derivative of Vari Fluor. Vari Fluor carboxylic acid derivatives are unactivated labeled fluorescent dyes for protein, antibody, and polysaccharide labeling that require carboxylic acid activation for use .
|
-

-
- HY-D1823
-
|
VF 647A carboxylic acid(free acid)
|
Fluorescent Dye
|
Others
|
|
Vari Fluor 647A Carboxylic acid (VF 647A Carboxylic acid) free acid is a carboxylic acid derivative of Vari Fluor. Vari Fluor carboxylic acid derivatives are unactivated labeled fluorescent dyes for protein, antibody, and polysaccharide labeling that require carboxylic acid activation for use .
|
-

-
- HY-D1828
-
|
VF 640 carboxylic acid(free acid)
|
Fluorescent Dye
|
Others
|
|
Vari Fluor 640 Carboxylic acid (VF 640 Carboxylic acid) free acid is a carboxylic acid derivative of Vari Fluor. Vari Fluor carboxylic acid derivatives are unactivated labeled fluorescent dyes for protein, antibody, and polysaccharide labeling that require carboxylic acid activation for use .
|
-

-
- HY-D1824
-
|
VF 488 carboxylic acid(free acid)
|
Fluorescent Dye
|
Others
|
|
Vari Fluor 488 Carboxylic acid (VF 488 Carboxylic acid) free acid is a carboxylic acid derivative of Vari Fluor. Vari Fluor carboxylic acid derivatives are unactivated labeled fluorescent dyes for protein, antibody, and polysaccharide labeling that require carboxylic acid activation for use .
|
-

-
- HY-D1825
-
|
VF 532 carboxylic acid(free acid)
|
Fluorescent Dye
|
Others
|
|
Vari Fluor 532 Carboxylic acid (VF 532 Carboxylic acid) free acid is a carboxylic acid derivative of Vari Fluor. Vari Fluor carboxylic acid derivatives are unactivated labeled fluorescent dyes for protein, antibody, and polysaccharide labeling that require carboxylic acid activation for use .
|
-

-
- HY-D1826
-
|
VF 594 carboxylic acid(free acid)
|
Fluorescent Dye
|
Others
|
|
Vari Fluor 594 Carboxylic acid (VF 594 Carboxylic acid) free acid is a carboxylic acid derivative of Vari Fluor. Vari Fluor carboxylic acid derivatives are unactivated labeled fluorescent dyes for protein, antibody, and polysaccharide labeling that require carboxylic acid activation for use .
|
-

-
- HY-D1827
-
|
VF 660 carboxylic acid(free acid)
|
Fluorescent Dye
|
Others
|
|
Vari Fluor 660 Carboxylic acid (VF 660 Carboxylic acid) free acid is a carboxylic acid derivative of Vari Fluor. Vari Fluor carboxylic acid derivatives are unactivated labeled fluorescent dyes for protein, antibody, and polysaccharide labeling that require carboxylic acid activation for use .
|
-

-
- HY-D1829
-
|
VF 568 carboxylic acid(free acid)
|
Fluorescent Dye
|
Others
|
|
Vari Fluor 568 Carboxylic acid (VF 568 Carboxylic acid) free acid is a carboxylic acid derivative of Vari Fluor. Vari Fluor carboxylic acid derivatives are unactivated labeled fluorescent dyes for protein, antibody, and polysaccharide labeling that require carboxylic acid activation for use .
|
-

-
- HY-D1830
-
|
VF 680 carboxylic acid(free acid)
|
Fluorescent Dye
|
Others
|
|
Vari Fluor 680 Carboxylic acid (VF 680 Carboxylic acid) free acid is a carboxylic acid derivative of Vari Fluor. Vari Fluor carboxylic acid derivatives are unactivated labeled fluorescent dyes for protein, antibody, and polysaccharide labeling that require carboxylic acid activation for use .
|
-

-
- HY-130695
-
|
|
PROTAC Linkers
|
Cancer
|
|
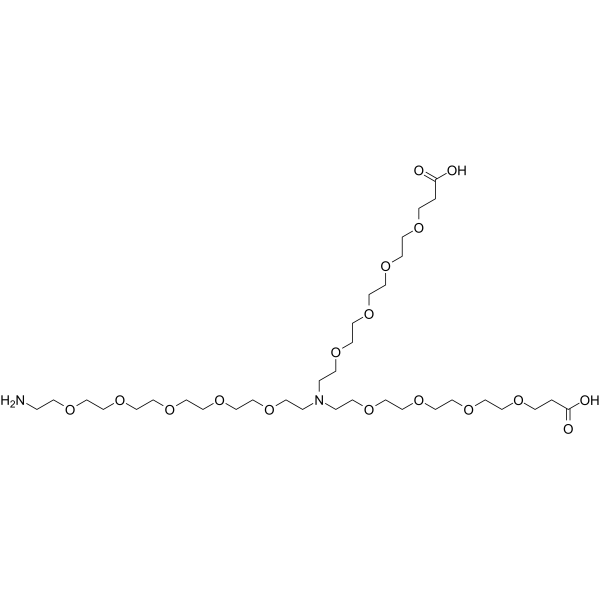
N-(Amino-PEG5)-N-bis(PEG4-acid) is a PEG-based PROTAC linker used in the synthesis of PROTACs. N-(Amino-PEG5)-N-bis(PEG4-acid) contains an amino group with two terminal carboxylic acids .
|
-
-
- HY-D1319
-
|
Cy5 acid chloride
|
Fluorescent Dye
|
Others
|
|
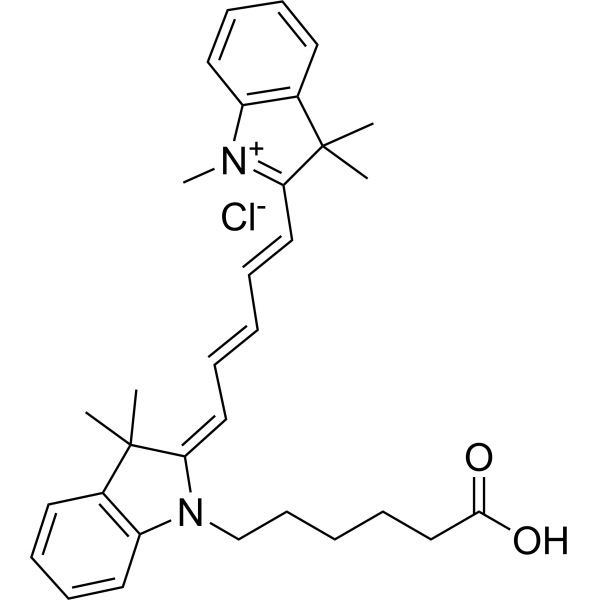
Cyanine5 carboxylic acid chloride (Cy5 acid chloride) is a fluorescent dye containing a non-activated carboxylic acid (Ex=646 nm, Em=662 nm). Cyanine5 carboxylic acid chloride is an non-reactive dye that can be used in control samples .
|
-
-
- HY-D2176
-
|
|
Fluorescent Dye
|
Others
|
|
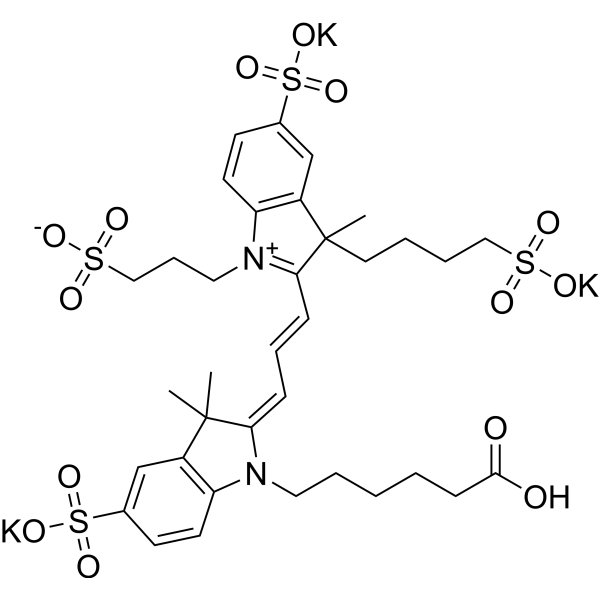
AF 555 carboxylic acid is a derivative of the orange fluorescent dye AF 555. AF 555 has a maximum emission wavelength of ~555 nm. AF 555 carboxylic acid is widely used in cell dyes, biological dyes, biomolecules and particle fluorescent labeling.
|
-
-
- HY-23212A
-
|
|
Others
|
Cancer
|
|
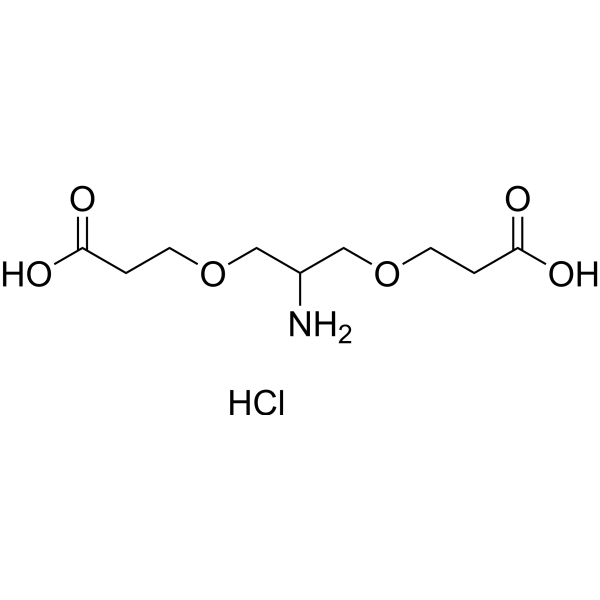
2-Amino-1,3-bis(carboxylethoxy)propane hydrochloride is a non-protein amino acid, sulfamic acid.2-Amino-1,3-bis(carboxylethoxy)propane hydrochloride contains one amino group and two terminal carboxylic acids.2-Amino-1,3-bis(carboxylethoxy)propane hydrochloride has a variety of physiological functions, including maintaining the stability of cell membranes, regulating cholesterol metabolism, supporting the normal function of the nervous system, participating in collagen synthesis, and anti-oxidation .
|
-
-
- HY-N1272
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
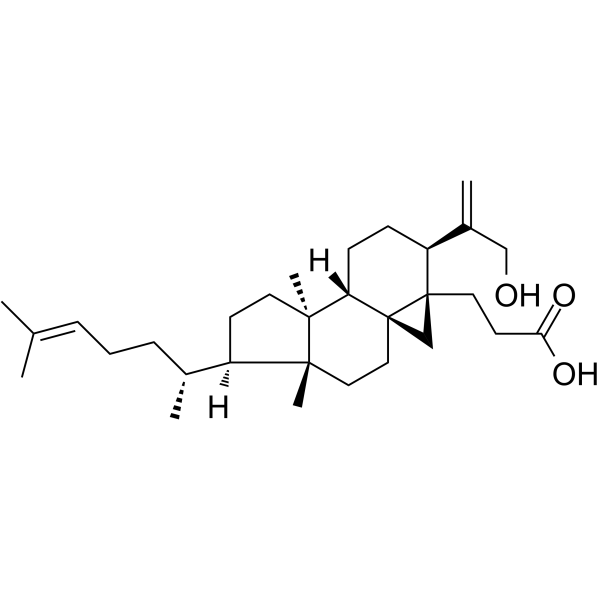
Secaubryenol is a class of 3,4-secocycloartane triterpenes isolated from Coussarea macrophylla. Secaubryenol does not display any cytotoxic effect at a dose of 10 µg/mL .
|
-
-
- HY-W127715
-
|
|
Fluorescent Dye
|
Others
|
|
Lucifer Yellow CH dipotassium is a high-intensity fluorescent probe containing free hydrazyl groups. Lucifer Yellow CH can react with fatty aldehydes at room temperature. Lucifer Yellow CH serves as a biological tracer to monitor neuronal branching, regeneration, gap junction detection and characterization, and selective ablation of cells after aldehyde fixation. Lucifer yellow CH displays the maximum excitation/emission of 430 nm/540 nm, respectively .
|
-
-
- HY-148377
-
|
|
Others
|
Cancer
|
|
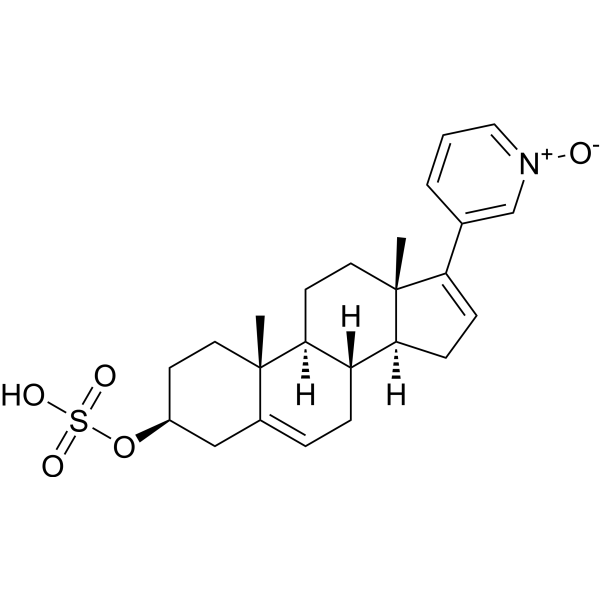
Abiraterone sulfate N-oxide is a carboxylic acid. Abiraterone sulfate N-oxide also is a major metabolite of Abiraterone (HY-70013). Abiraterone sulfate N-oxide can be used for the research of prostate cancer .
|
-
-
- HY-141147
-
|
|
Drug-Linker Conjugates for ADC
|
Cancer
|
|
7-O-(Amino-PEG4)-paclitaxel is a PEG-class Drug-linker conjugates for ADC, containing a paclitaxel moiety and a amino group. The amine group is reactive with carboxylic acids, activated NHS esters, carbonyls (ketone, aldehyde) etc. 7-O-(Amino-PEG4)-paclitaxel can be used in the synthesis of Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs) .
|
-
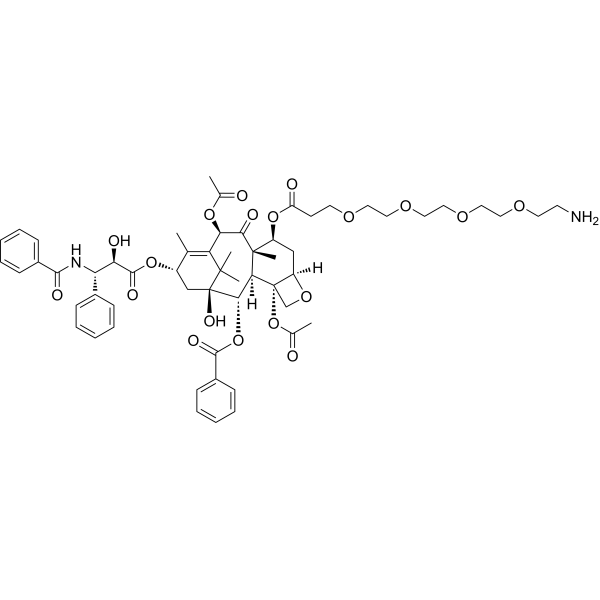
-
- HY-141148
-
|
|
Drug-Linker Conjugates for ADC
|
Cancer
|
|
7-O-(Cbz-N-amido-PEG4)-paclitaxel is a PEG-class Drug-linker conjugates for ADC, containing a paclitaxel moiety and a amino group. The amine group is reactive with carboxylic acids, activated NHS esters, carbonyls (ketone, aldehyde) etc. 7-O-(Cbz-N-amido-PEG4)-paclitaxel can be used in the synthesis of Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs) .
|
-
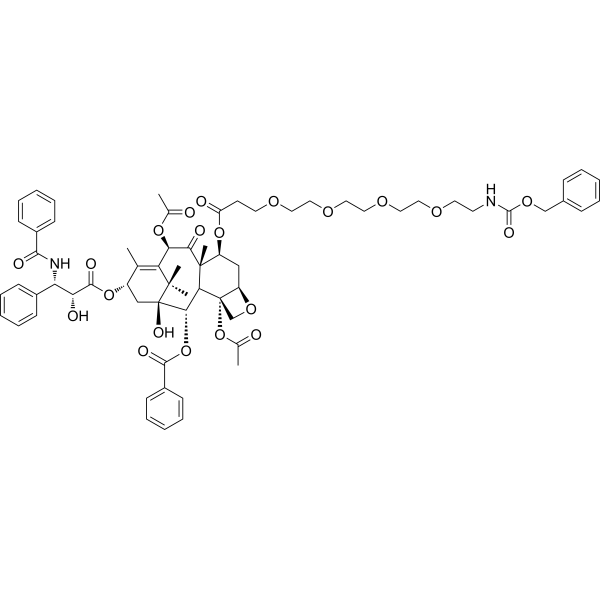
-
- HY-N7692
-
|
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
Polyporusterone A is a triterpene carboxylic acid isolated from Polyporus umbellatus Fries. Polyporusterone A has inhibitory effect on free radical-induced lysis of red blood cells (hemolysis) .
|
-
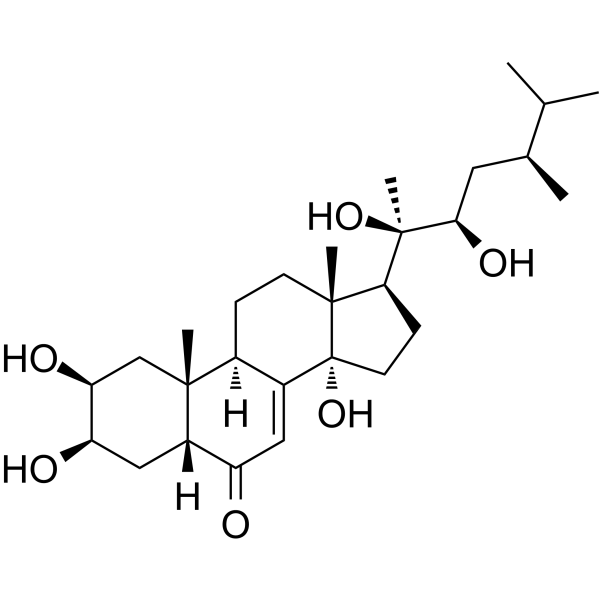
-
- HY-N7693
-
|
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
Polyporusterone B is a triterpene carboxylic acid isolated from Polyporus umbellatus Fries. Polyporusterone B has inhibitory effect on free radical-induced lysis of red blood cells (hemolysis) .
|
-
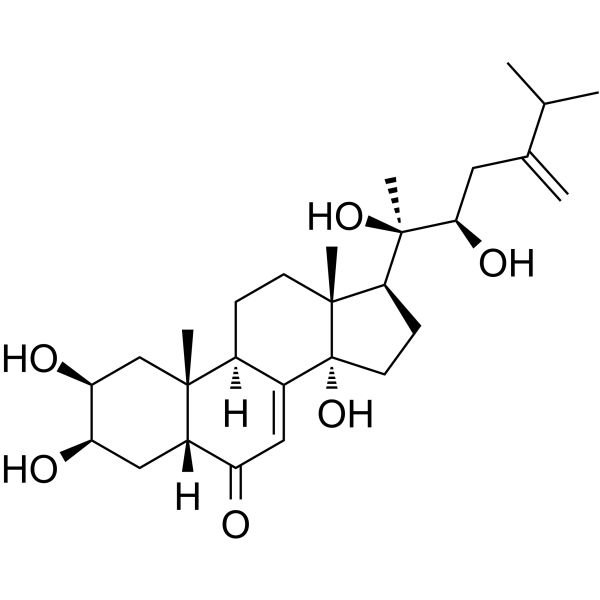
-
- HY-W403633
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
Hexahydrohippuric acid is a metabolite of Shikimate acid in both liver and kidney, under microbial metabolism effect. Hexahydrohippuric acid is made of cyclohexane carboxylic acid and glycinamide, and shows antibacterial activity .
|
-
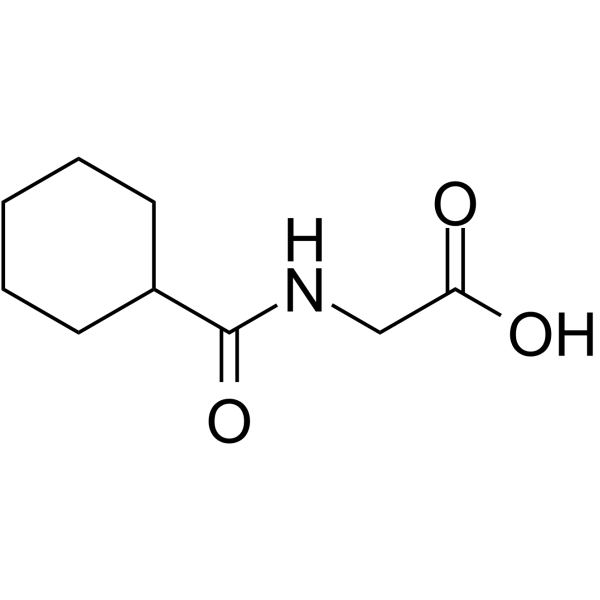
-
- HY-148087
-
|
|
RXFP Receptor
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
AZD5462 is a RXFP1 modulator, can be used for heart failure research. RXFP1 is the cognate receptor for human relaxin, belongs to GPCR family 1c number with anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory properties .
|
-
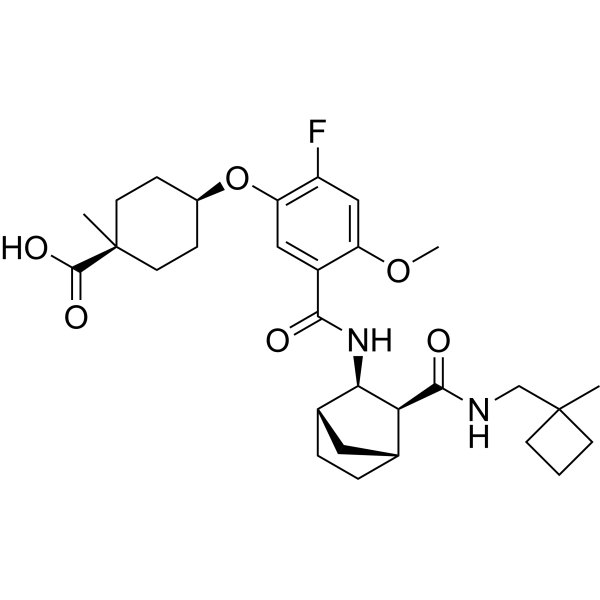
-
- HY-W017386
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid, sodium salt belongs to the class of carboxylic acids, consisting of a five-carbon chain with methyl, carboxyl and ketone groups. This compound is commonly used as an analytical reagent in biochemical and medical research, especially for the detection and quantification of 2-ketoacids. It can also be used as a substrate in enzyme assays to measure the activity of certain enzymes involved in amino acid metabolism. In addition, 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid, sodium salt may have potential research roles in various diseases such as diabetes, cancer and cardiovascular disease.
|
-
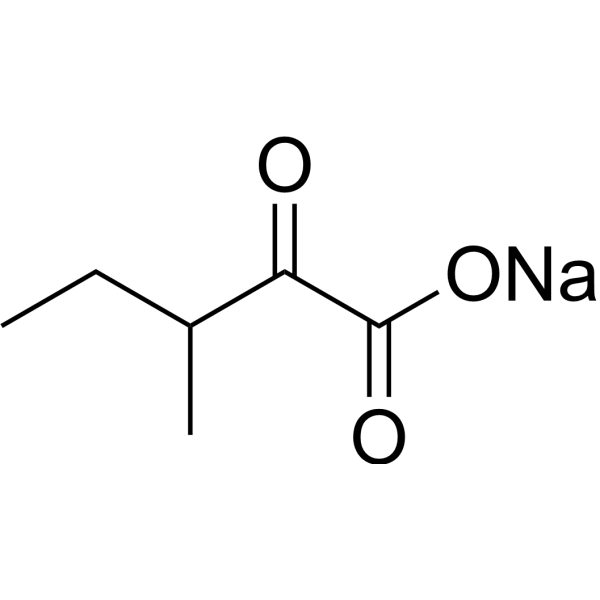
-
- HY-W010361
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Tetramethylammonium acetate is an organic compound commonly used as a phase transfer catalyst in organic synthesis reactions, especially those involving charged species or polar reagents. It can facilitate the transfer of reactants between two immiscible phases, such as water and organic solvents, by forming stable ion pairs. Additionally, Tetramethylammonium acetate has been used to prepare a variety of organic compounds, including esters, amides, and carboxylic acids. Due to its unique physicochemical properties, it has also been investigated for its potential use in developing new materials such as ionic liquids and liquid crystals. "x" in the formula represents the number of water molecules in the crystal structure, which can vary depending on the preparation method.
|
-
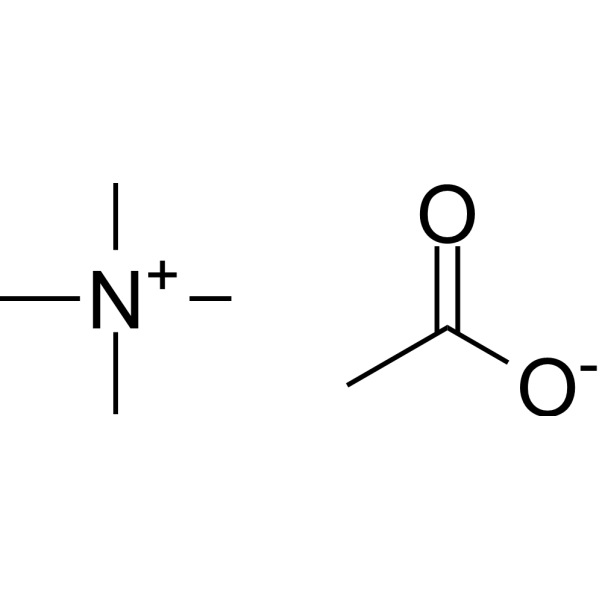
-
- HY-145243
-
|
|
Apoptosis
|
Others
|
|
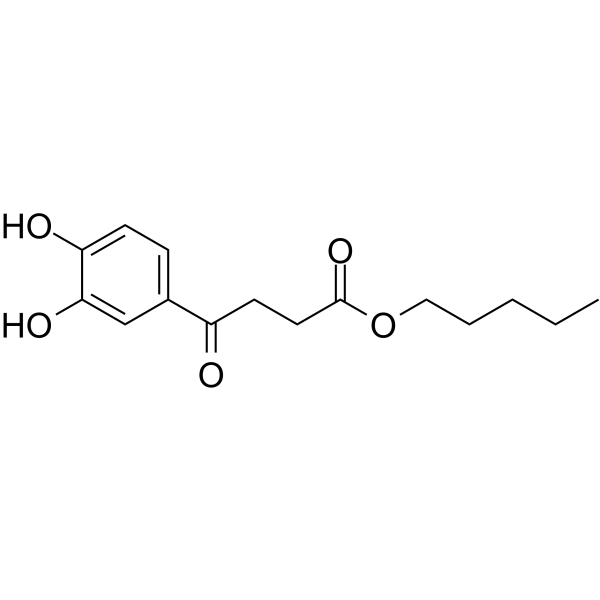
PDPOB is a phenyl carboxylic acid derivative. PDPOB displays protective roles against OGD/R-evoked multiaspect neuronal deterioration in SH-SY5Y cells, as evidenced by alleviated mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. PDPOB has the potential for the research of cerebral ischemia .
|
-
-
- HY-162125
-
|
|
Angiotensin Receptor
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
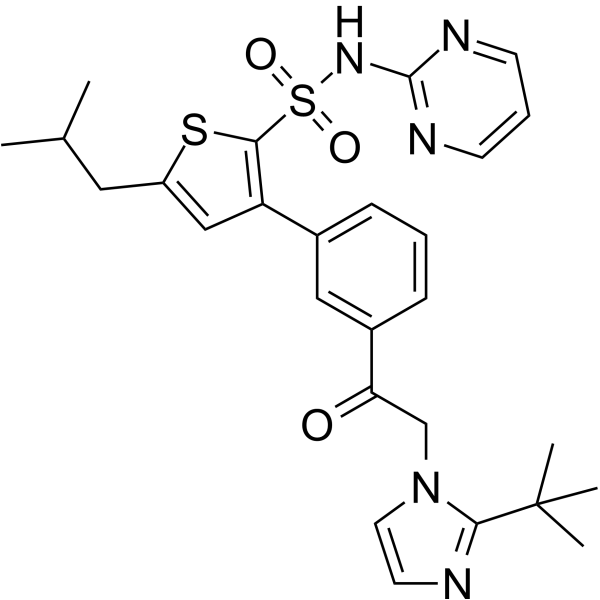
AT2 receptor ligand-1(compound 14) is a potent angiotensin AT2 receptor ligand with the Ki 4.9 nM. AT2 receptor ligand-1 shows high stability in microsomes of the sulfonamide ligands .
|
-
-
- HY-D1650
-
|
|
Fluorescent Dye
|
Others
|
|
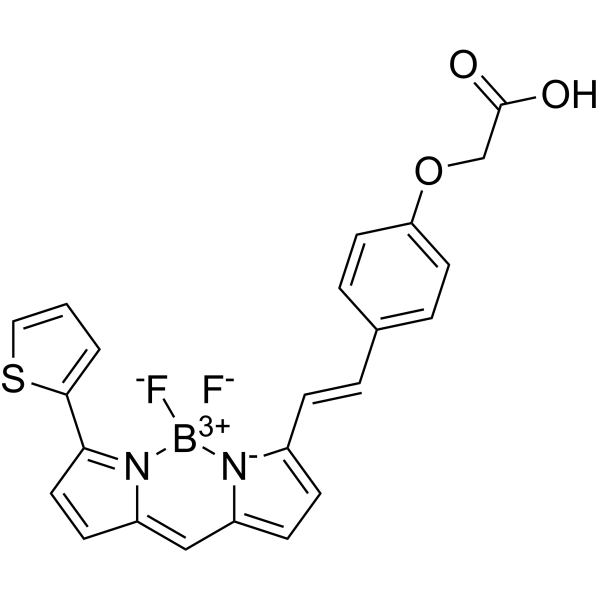
BDP 630/650 carboxylic acid is a bright far-red fluorophore based on a borondipyrromethene scaffold. BDP 630/650 carboxylic acid is a BDP linker containing carboxylic acid. BDP 630/650 carboxylic acid can react with primary amine groups to form a stable amide bond. (λex=630 nm, λem=650 nm) .
|
-
-
- HY-120973
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
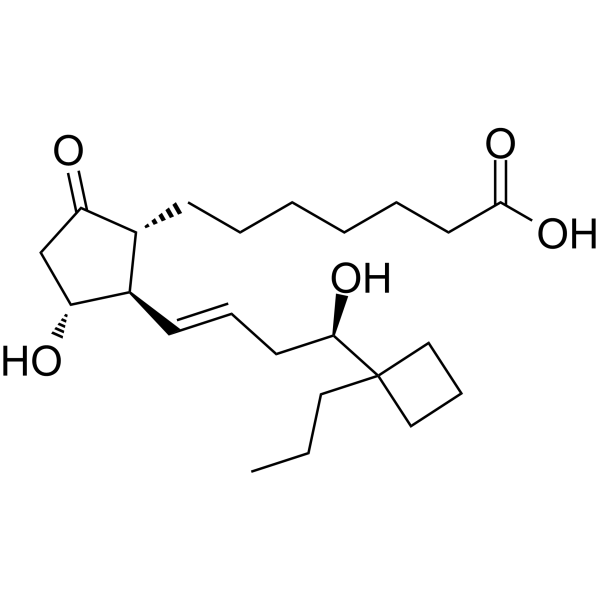
(R)-Butaprost (free acid). Butaprost is a structural analog of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) with good selectivity for the EP2 receptor subtype. Butaprost is frequently used pharmacologically to define the expression profile of EP receptors in various human and animal tissues and cells. Gardiner caused serious confusion about the structure of butaprost in 1986 when he reported that the epimer of butaprost showing this selective activity was the C-16 (R)-epimer ( See reference 2 and notes). To increase the binding affinity of (R)-butaprost to prostaglandin receptors, we removed the methyl ester of (R)-butaprost and recreated the native C-1 carboxylic acid. Prostaglandin free acids typically bind their cognate receptors with 10 to 100-fold higher affinity than the corresponding ester derivatives. The pharmacology of (R)-butaprost has not been carefully studied, but it is generally considered to be the less active C-16 epimer. (Note: In the 1986 Gardiner paper in the British Journal of Pharmacology, butaprost appears on page 46 under the designation TR 4979. The structure drawn is incorrect because the authors use and refer to the more active C - The 16 epimer, which is actually 16(S). The structure on page 46 shows the structure as 16(R). It was not until the late 1990s that careful studies in the United States and Japan correctly determined the actual structure of C-16 The type is 16(S) in a compound called butaprost.)
|
-
-
-
HY-L0101V
-
|
|
2,244,487 compounds
|
|
FCH Group Screening Library Collection contains about 2,244,487 lead-like compounds for biological screening. This brand new collection comprises polar molecules with pharmacologically important groups such as free carboxylic and amino groups.
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Type |
-
- HY-W269179
-
|
|
Fluorescent Dyes/Probes
|
|
4-Bromomethyl-6,7-dimethoxycoumarin is a fluorescent label for carboxylic acids in chromatographic detection .
|
-
- HY-D0035
-
|
|
Fluorescent Dyes/Probes
|
|
MPAC-Br is a highly sensitive fluorescent derivatization reagent for carboxylic acids in HPLC .
|
-
- HY-D0115
-
|
|
Fluorescent Dyes/Probes
|
|
7-Hydroxycoumarin-3-carboxylic acid N-succinimidyl ester is the amine-reactive succinimidyl ester of 7-Hydroxycoumarin-3-carboxylic acid. 7-Hydroxycoumarin-3-carboxylic acid N-succinimidyl ester is a blue fluorescent dye for labeling proteins and nucleic acids .
|
-
- HY-D1970
-
|
|
Fluorescent Dyes/Probes
|
|
ATTO 700 Cadaverin is a cadaverine derivative of ATTO 700 for reactions of carboxylic acids, aldehydes and ketones with maximum excitation/emission wavelengths: 700/716 nm.
|
-
- HY-D1658
-
|
|
Fluorescent Dyes/Probes
|
|
BDP 581/591 amine hydrochloride is a BODIPY dye linker. BDP 581/591 is a universal, photostable fluorophore. The addition of the amine group allows for the compound to react with carboxylic acids, activated NHS esters and other carbonyl groups .
|
-
- HY-D0036
-
|
4-Bromomethyl-7-methoxycoumarin
|
Fluorescent Dyes/Probes
|
|
Br-Mmc (4-Bromomethyl-7-methoxycoumarin) is often used as fluorescent label for the determination of compounds possessing a carboxylic group. Br-Mmc is used for the determination fatty acids by TLC or HPLC .
|
-
- HY-D1821
-
|
VF 750 carboxylic acid(free acid)
|
Dyes
|
|
Vari Fluor 750 Carboxylic acid (VF 750 Carboxylic acid) free acid is a carboxylic acid derivative of Vari Fluor. Vari Fluor carboxylic acid derivatives are unactivated labeled fluorescent dyes for protein, antibody, and polysaccharide labeling that require carboxylic acid activation for use .
|
-
- HY-D1822
-
|
VF 555 carboxylic acid(free acid)
|
Dyes
|
|
Vari Fluor 555 Carboxylic acid (VF 555 Carboxylic acid) free acid is a carboxylic acid derivative of Vari Fluor. Vari Fluor carboxylic acid derivatives are unactivated labeled fluorescent dyes for protein, antibody, and polysaccharide labeling that require carboxylic acid activation for use .
|
-
- HY-D1823
-
|
VF 647A carboxylic acid(free acid)
|
Dyes
|
|
Vari Fluor 647A Carboxylic acid (VF 647A Carboxylic acid) free acid is a carboxylic acid derivative of Vari Fluor. Vari Fluor carboxylic acid derivatives are unactivated labeled fluorescent dyes for protein, antibody, and polysaccharide labeling that require carboxylic acid activation for use .
|
-
- HY-D1828
-
|
VF 640 carboxylic acid(free acid)
|
Dyes
|
|
Vari Fluor 640 Carboxylic acid (VF 640 Carboxylic acid) free acid is a carboxylic acid derivative of Vari Fluor. Vari Fluor carboxylic acid derivatives are unactivated labeled fluorescent dyes for protein, antibody, and polysaccharide labeling that require carboxylic acid activation for use .
|
-
- HY-D1824
-
|
VF 488 carboxylic acid(free acid)
|
Dyes
|
|
Vari Fluor 488 Carboxylic acid (VF 488 Carboxylic acid) free acid is a carboxylic acid derivative of Vari Fluor. Vari Fluor carboxylic acid derivatives are unactivated labeled fluorescent dyes for protein, antibody, and polysaccharide labeling that require carboxylic acid activation for use .
|
-
- HY-D1825
-
|
VF 532 carboxylic acid(free acid)
|
Dyes
|
|
Vari Fluor 532 Carboxylic acid (VF 532 Carboxylic acid) free acid is a carboxylic acid derivative of Vari Fluor. Vari Fluor carboxylic acid derivatives are unactivated labeled fluorescent dyes for protein, antibody, and polysaccharide labeling that require carboxylic acid activation for use .
|
-
- HY-D1826
-
|
VF 594 carboxylic acid(free acid)
|
Dyes
|
|
Vari Fluor 594 Carboxylic acid (VF 594 Carboxylic acid) free acid is a carboxylic acid derivative of Vari Fluor. Vari Fluor carboxylic acid derivatives are unactivated labeled fluorescent dyes for protein, antibody, and polysaccharide labeling that require carboxylic acid activation for use .
|
-
- HY-D1827
-
|
VF 660 carboxylic acid(free acid)
|
Dyes
|
|
Vari Fluor 660 Carboxylic acid (VF 660 Carboxylic acid) free acid is a carboxylic acid derivative of Vari Fluor. Vari Fluor carboxylic acid derivatives are unactivated labeled fluorescent dyes for protein, antibody, and polysaccharide labeling that require carboxylic acid activation for use .
|
-
- HY-D1829
-
|
VF 568 carboxylic acid(free acid)
|
Dyes
|
|
Vari Fluor 568 Carboxylic acid (VF 568 Carboxylic acid) free acid is a carboxylic acid derivative of Vari Fluor. Vari Fluor carboxylic acid derivatives are unactivated labeled fluorescent dyes for protein, antibody, and polysaccharide labeling that require carboxylic acid activation for use .
|
-
- HY-D1830
-
|
VF 680 carboxylic acid(free acid)
|
Dyes
|
|
Vari Fluor 680 Carboxylic acid (VF 680 Carboxylic acid) free acid is a carboxylic acid derivative of Vari Fluor. Vari Fluor carboxylic acid derivatives are unactivated labeled fluorescent dyes for protein, antibody, and polysaccharide labeling that require carboxylic acid activation for use .
|
-
- HY-D1319
-
|
Cy5 acid chloride
|
Fluorescent Dyes/Probes
|
|
Cyanine5 carboxylic acid chloride (Cy5 acid chloride) is a fluorescent dye containing a non-activated carboxylic acid (Ex=646 nm, Em=662 nm). Cyanine5 carboxylic acid chloride is an non-reactive dye that can be used in control samples .
|
-
- HY-D2176
-
|
|
Fluorescent Dyes/Probes
|
|
AF 555 carboxylic acid is a derivative of the orange fluorescent dye AF 555. AF 555 has a maximum emission wavelength of ~555 nm. AF 555 carboxylic acid is widely used in cell dyes, biological dyes, biomolecules and particle fluorescent labeling.
|
-
- HY-W127715
-
|
|
Fluorescent Dyes/Probes
|
|
Lucifer Yellow CH dipotassium is a high-intensity fluorescent probe containing free hydrazyl groups. Lucifer Yellow CH can react with fatty aldehydes at room temperature. Lucifer Yellow CH serves as a biological tracer to monitor neuronal branching, regeneration, gap junction detection and characterization, and selective ablation of cells after aldehyde fixation. Lucifer yellow CH displays the maximum excitation/emission of 430 nm/540 nm, respectively .
|
-
- HY-D1650
-
|
|
Fluorescent Dyes/Probes
|
|
BDP 630/650 carboxylic acid is a bright far-red fluorophore based on a borondipyrromethene scaffold. BDP 630/650 carboxylic acid is a BDP linker containing carboxylic acid. BDP 630/650 carboxylic acid can react with primary amine groups to form a stable amide bond. (λex=630 nm, λem=650 nm) .
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Type |
-
- HY-P2947
-
|
Aldehyde dehydrogenase (NAD(P))
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
ALDH (Aldehyde dehydrogenase (NAD(P))) catalyzes the oxidation of aldehydes into their corresponding carboxylic acids with the concomitant reduction of the cofactor NAD(P) into NAD(P)H, is often used in biochemical studies. The ALDHs are one of many enzyme systems the body utilizes to alleviate aldehyde stress .
|
-
- HY-W017386
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid, sodium salt belongs to the class of carboxylic acids, consisting of a five-carbon chain with methyl, carboxyl and ketone groups. This compound is commonly used as an analytical reagent in biochemical and medical research, especially for the detection and quantification of 2-ketoacids. It can also be used as a substrate in enzyme assays to measure the activity of certain enzymes involved in amino acid metabolism. In addition, 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid, sodium salt may have potential research roles in various diseases such as diabetes, cancer and cardiovascular disease.
|
-
- HY-128851A
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Coenzyme A (CoASH) is a ubiquitous and essential cofactor, which is an acyl group carrier and carbonyl-activating group for the citric acid cycle and fatty acid metabolism. Coenzyme A plays a central role in the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle and the metabolism of carboxylic acids, including short- and long-chain fatty acids .
|
-
- HY-128851B
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Coenzyme A (CoASH) sodium is a ubiquitous and essential cofactor, which is an acyl group carrier and carbonyl-activating group for the citric acid cycle and fatty acid metabolism. Coenzyme A plays a central role in the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle and the metabolism of carboxylic acids, including short- and long-chain fatty acids .
|
-
- HY-P2736
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Amidases, a member of nitrilase superfamily, catalyzes the hydrolysis of an amide, leading to the formation of carboxylic acid and ammonia. Amidases contain a conserved stretch of approximately 130 amino acids known as the AS sequence, and play a role in important metabolic processes .
|
-
- HY-W010361
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Tetramethylammonium acetate is an organic compound commonly used as a phase transfer catalyst in organic synthesis reactions, especially those involving charged species or polar reagents. It can facilitate the transfer of reactants between two immiscible phases, such as water and organic solvents, by forming stable ion pairs. Additionally, Tetramethylammonium acetate has been used to prepare a variety of organic compounds, including esters, amides, and carboxylic acids. Due to its unique physicochemical properties, it has also been investigated for its potential use in developing new materials such as ionic liquids and liquid crystals. "x" in the formula represents the number of water molecules in the crystal structure, which can vary depending on the preparation method.
|
-
- HY-120973
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
(R)-Butaprost (free acid). Butaprost is a structural analog of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) with good selectivity for the EP2 receptor subtype. Butaprost is frequently used pharmacologically to define the expression profile of EP receptors in various human and animal tissues and cells. Gardiner caused serious confusion about the structure of butaprost in 1986 when he reported that the epimer of butaprost showing this selective activity was the C-16 (R)-epimer ( See reference 2 and notes). To increase the binding affinity of (R)-butaprost to prostaglandin receptors, we removed the methyl ester of (R)-butaprost and recreated the native C-1 carboxylic acid. Prostaglandin free acids typically bind their cognate receptors with 10 to 100-fold higher affinity than the corresponding ester derivatives. The pharmacology of (R)-butaprost has not been carefully studied, but it is generally considered to be the less active C-16 epimer. (Note: In the 1986 Gardiner paper in the British Journal of Pharmacology, butaprost appears on page 46 under the designation TR 4979. The structure drawn is incorrect because the authors use and refer to the more active C - The 16 epimer, which is actually 16(S). The structure on page 46 shows the structure as 16(R). It was not until the late 1990s that careful studies in the United States and Japan correctly determined the actual structure of C-16 The type is 16(S) in a compound called butaprost.)
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Area |
-
- HY-P2736
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
Amidases, a member of nitrilase superfamily, catalyzes the hydrolysis of an amide, leading to the formation of carboxylic acid and ammonia. Amidases contain a conserved stretch of approximately 130 amino acids known as the AS sequence, and play a role in important metabolic processes .
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Category |
Target |
Chemical Structure |
Your information is safe with us. * Required Fields.
Inquiry Information
- Product Name:
- Cat. No.:
- Quantity:
- MCE Japan Authorized Agent: